Introduction of three ways turn Waste to energy conversion technology
Industry News / Chat online / Give me a price / November 9, 2017
Waste is one of the major challenges modern world is facing today. Every year billions tones of waste are generated and these amounts are rising steadily. In spite of the reasonably successful 3R strategy (Reduce-Recover-Recycle) to reduce landfill volumes, there are still significant quantities of waste to be disposed.
Wastes such as MSW, ASR, electronic waste are currently either difficult to recycle or not 100% recyclable, while other waste such as medical waste is not recyclable and shall be disposed. Another typical example is goods packaging, when plastic attached to other materials (aluminum / polymer laminate). This laminate is inseparable from paper at the recycling facility. All these cases result in either landfilling or incineration.
Consequently, waste disposal can cause negative impacts on health and the environment, including pollutions to air and water. Waste also represents a loss of natural resources (such as the metals or other recyclable materials it contains, or its potential as an energy source). Therefore, proper waste treatment can protect public health and the quality of the environment whilst supporting conservation of natural resources. Moreover many countries introduced promotion instrument for generating electricity from non-fossil resources.
Here are three methods (Gasification, Incineration and Pyrolysis) will waste energy conversion technology is introduced.
Gasification is the thermal conversion of waste under conditions of the limited oxygen supply. Energy of the produced syngas is used to generate electricity. Practical applicability of gasification depends on waste to be treated since gasification technology is limited by several main operating issues, such as feed size limitations, high particle loading, tar formation, etc. High temperature waste conversion using plasma arc, also results in gas and solid slag. Life of liners and torch as well as high energy consumption make plasma gasification technology not commercially viable.
Incineration is the oldest alternative to a landfill disposal - high temperature combustion of waste (at 850 C and higher) with sufficient supply of oxygen. Energy of hot gases is used to generate steam and, consequently, to generate electricity by a steam turbine. Incineration consumes fuel to maintain stable combustion of waste. Besides that the process suffers from several issues such as generation of large amount of gas emissions and carbon dioxide in particular, dioxins emerging, dust filtering, difficulties in handling of high caloric waste as plastics, ASR, e-waste.
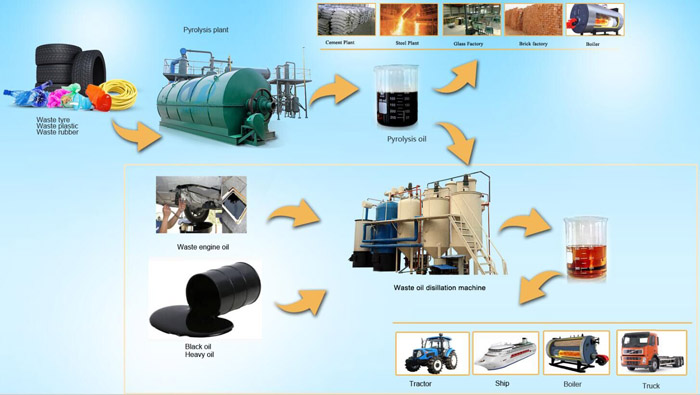
Pyrolysis technology
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of waste in the absence of the external oxygen supply. The pyrolysis process takes place under the temperatures typically around 500 C. The gaseous product of pyrolysis can undergo one of the following transformations in downstream processes:
Cooling down followed by oil condensing; liquefaction is applicable for a limited number of feedstock, such as plastics or rubber;Cracking and cleaning in order to be used as fuel in a gas engine; pyrolysis gas conditioning is a complicated problem and additional drawback is that further treatment of the pyrolysis char will be performed at the high temperatures around 1500 C (maintenance issues);Secondary combustion in a boiler to generate the steam, which consequently will be sent to steam turbine to generate electricity; further enhancing steam cycle allows combining simplicity and reliability in operation with the improved energy generation.
Wastes such as MSW, ASR, electronic waste are currently either difficult to recycle or not 100% recyclable, while other waste such as medical waste is not recyclable and shall be disposed. Another typical example is goods packaging, when plastic attached to other materials (aluminum / polymer laminate). This laminate is inseparable from paper at the recycling facility. All these cases result in either landfilling or incineration.
Consequently, waste disposal can cause negative impacts on health and the environment, including pollutions to air and water. Waste also represents a loss of natural resources (such as the metals or other recyclable materials it contains, or its potential as an energy source). Therefore, proper waste treatment can protect public health and the quality of the environment whilst supporting conservation of natural resources. Moreover many countries introduced promotion instrument for generating electricity from non-fossil resources.
Here are three methods (Gasification, Incineration and Pyrolysis) will waste energy conversion technology is introduced.
Gasification is the thermal conversion of waste under conditions of the limited oxygen supply. Energy of the produced syngas is used to generate electricity. Practical applicability of gasification depends on waste to be treated since gasification technology is limited by several main operating issues, such as feed size limitations, high particle loading, tar formation, etc. High temperature waste conversion using plasma arc, also results in gas and solid slag. Life of liners and torch as well as high energy consumption make plasma gasification technology not commercially viable.
Incineration is the oldest alternative to a landfill disposal - high temperature combustion of waste (at 850 C and higher) with sufficient supply of oxygen. Energy of hot gases is used to generate steam and, consequently, to generate electricity by a steam turbine. Incineration consumes fuel to maintain stable combustion of waste. Besides that the process suffers from several issues such as generation of large amount of gas emissions and carbon dioxide in particular, dioxins emerging, dust filtering, difficulties in handling of high caloric waste as plastics, ASR, e-waste.

Pyrolysis technology
Cooling down followed by oil condensing; liquefaction is applicable for a limited number of feedstock, such as plastics or rubber;Cracking and cleaning in order to be used as fuel in a gas engine; pyrolysis gas conditioning is a complicated problem and additional drawback is that further treatment of the pyrolysis char will be performed at the high temperatures around 1500 C (maintenance issues);Secondary combustion in a boiler to generate the steam, which consequently will be sent to steam turbine to generate electricity; further enhancing steam cycle allows combining simplicity and reliability in operation with the improved energy generation.
contact us
- QWhat raw material do you plan to process?
- Rubber tire
- Waste plastic
- Oil sludge
- Biomass
- Waste oil
- Pyrolysis oil
- Not decided yet
- Other:
- QMachine daily processing capacity (tons of feedstock)
- 100kg-2ton
- 5-15ton
- 15-50ton
- >50ton
- Not decided yet
- QDesired final product and its primary applications